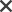Navigation maps or Flowcharts are used to depict the way people move through a website or application and gain insights on how they experience the product.
1. Represent each page or location of the design (website, app, route, etc) as a box. Connect the boxes to display how they connect to each other.
2. Go through the design and check if the ow of the different tasks is correct. Evaluate if the way the design works is logical for the users.
3. If needed, move the boxes around, delete some, add extra steps, etc. Once that is done go over the design again and check if it is logical.
4. Document the version(s) that you think work best for the users and the intended design.
WHEN
After identifying what steps the design needs, but when it is still in conceptual phase.
WHY
It allows to check the ow of the design and to make sure it is clear for users.
NOTE!
Structure boxes in a logical way, that gives you insight rather than confusion.
OUTPUT
An understanding on how many pages there are and the most logical flows.
Next
Take the concept and polish it, make a mid-high fidelity prototype.
Reference
BENYON, David. Designing interactive systems [Elektronisk resurs]: a comprehensive guide to HCI and interaction design. 2010./