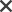A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
1. Brainstorm a list of design problems and write them down.
2. Sort the list by importance or degree of abstraction.
3. Write down the main problem close to the core branch, write the sublevel problems as branches of the problems they are related to.
WHEN
At the beginning of the project.
WHY
To have an overview of the problems faced.
NOTE!
It might help to write down each problem on a small piece of paper, so you can shuffle them easily. The hierarchy could be from important to less important, or abstract to practical.
OUTPUT
An overview of which problems are at the core of a project, and which are concrete.
Next
Solve the problems, try to start with core problems. If this isn’t possible, go further into a sub level.
Reference
HOVLAND, Ingie. Successful Communication. A Toolkit for Researchers and Civil Society Organisations. London: Overseas Development Institute, 2005./